Achondroplasia: another step forward in treatment
Today, several new molecules, some of which emanate directly from research on deregulated mechanisms in achondroplasia conducted at the Imagine Institute by Laurence Legeai Mallet and her team, are in clinical trials around the world.
Autisme : le point sur les troubles du spectre de l'autisme
This major communication disorder, which affects 700,000 people in France, can take different forms without necessarily being associated with an intellectual deficit. Since the mid-1990s, research on ASD has developed, clearly establishing that the mechanisms involved are varied, ranging from a single genetic mutation, to combinations of common genetic variants with rarer variants, and even to much more complex interactions between genetics and environment.
An update on research on epilepsies
Rare epilepsies in children are often accompanied by behavioral problems, psychiatric disorders, and cognitive and social disorders.” To date, there is no cure. The treatment mainly consists of controlling the seizures and associated problems, but the group of rare epilepsies presents high levels of resistance to any type of treatment.
Everything to know about celiac disease and its complications
Celiac disease affects 1% of the population. The only treatment for it is a strict gluten free diet. It cures symptoms and protects from complications, in particular osteoporosis, infertility, autoimmune diseases and malignancies.
Better understanding hereditary eye diseases
Jean-Michel Rozet studies congenital eye malformations, and degenerative disorders of the optic nerve and the photosensitive retina, for which treatment is in the very early stages at best, most often nonexistent.
Familial Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis
In patients with Familial Lymphohistiocytosis, when a virus enters the body, the T-cells that are responsible for killing virus-infected cells no longer perform this defense function properly, causing persistent fever, fatigue and irritability, accompanied by enlargement of the liver and spleen, and sometimes neurological disorders.
Dr. Nadine Cerf-Bensussan, director of the Intestinal Immunity Laboratory at the Imagine Institute, and Dr. Grégoire Michaux, director of research at the Institute of Genetics and Development in Rennes (CNRS), discuss research on the STXBP2 gene mutation which, by altering the functioning of the Munc-18-2 protein, leads to associated digestive symptoms.
Diabète rare monogénique de l'enfant
Advances in genetics are improving the diagnostic approach and the management of this diabetes that affects young children. New treatments are being tested in clinical trials and, for the first time, these treatments, without the use of insulin, do not cause hypoglycemia. This is an avenue that is being closely followed by these specialists in childhood diabetes.
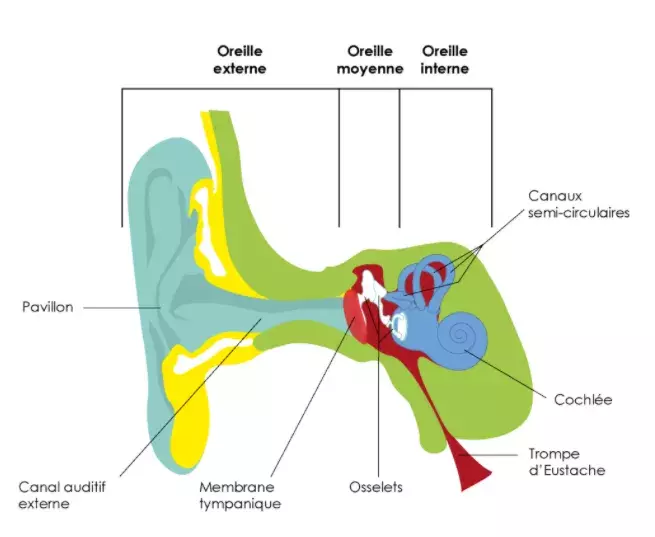
Genetic deafness: an update on these pathologies, research and care
It is estimated today that 80% of early-onset deafness is genetic in origin, with more than 120 genetic forms of deafness already identified and nearly 500 syndromes including deafness already described. Several teams at the Imagine Institute and on the campus of the Hôpital Necker-Enfants malades AP-HP are specialized in these deafnesses to better understand and manage them.